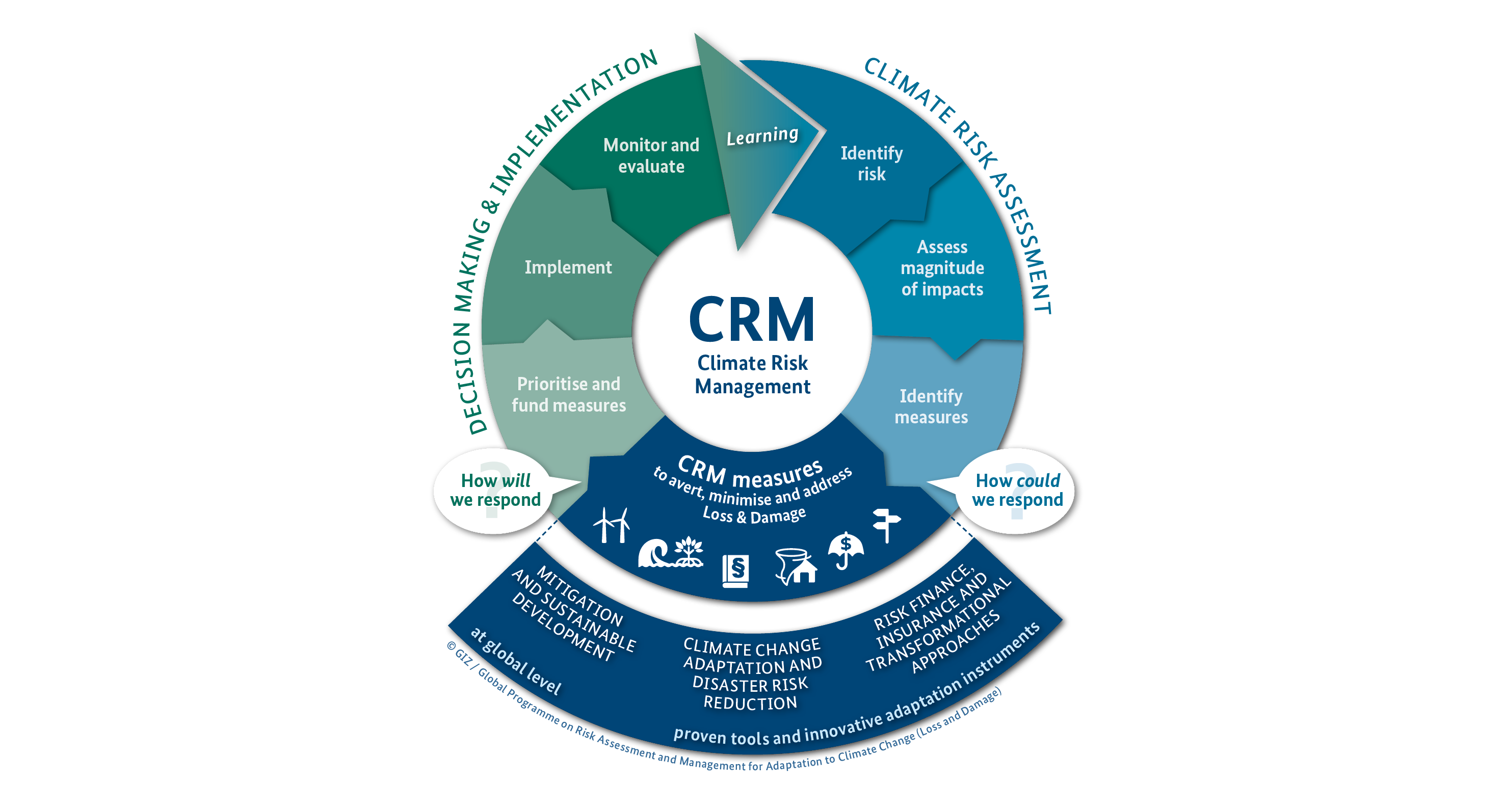
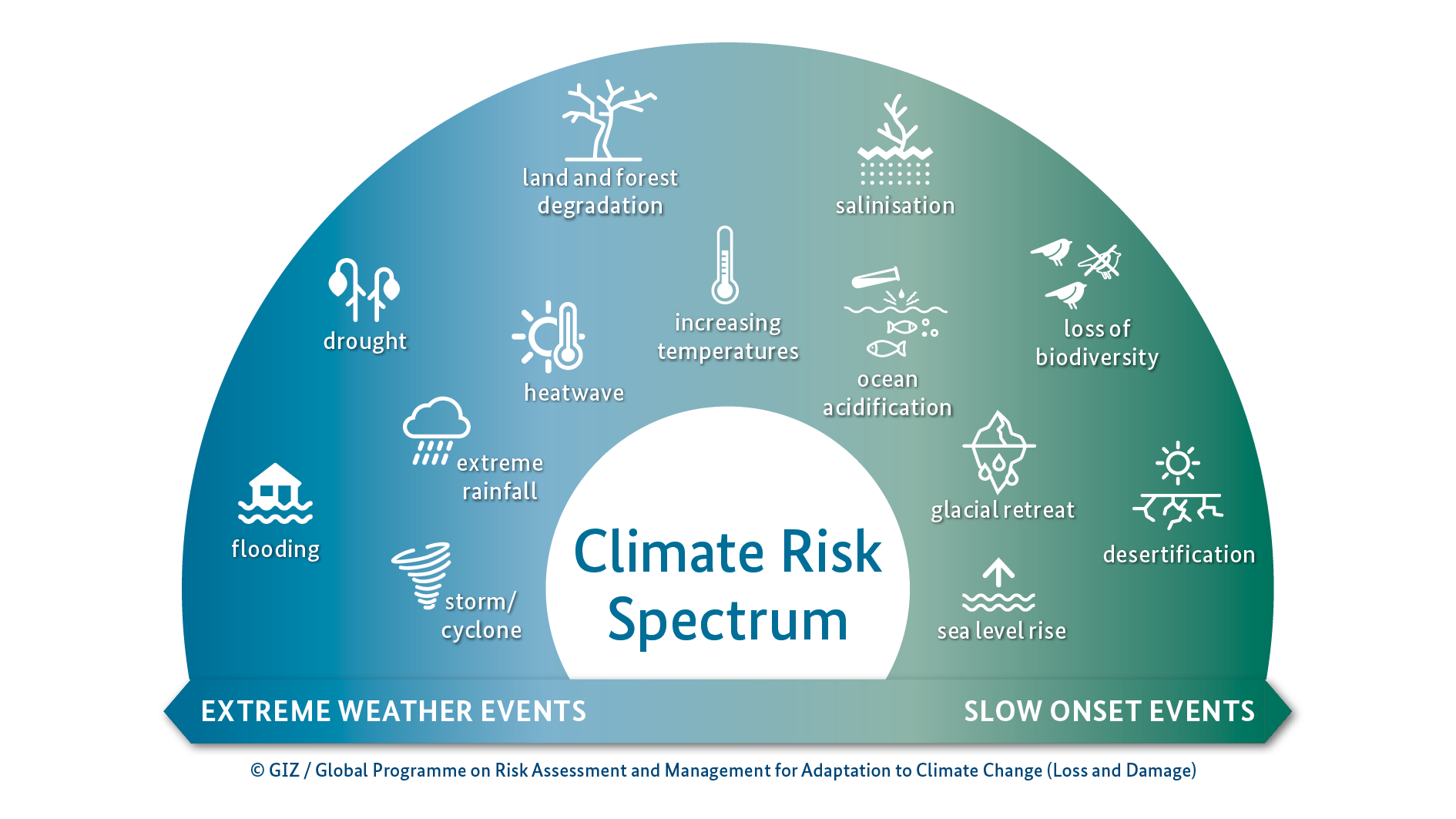
Integrated climate risk management cycle
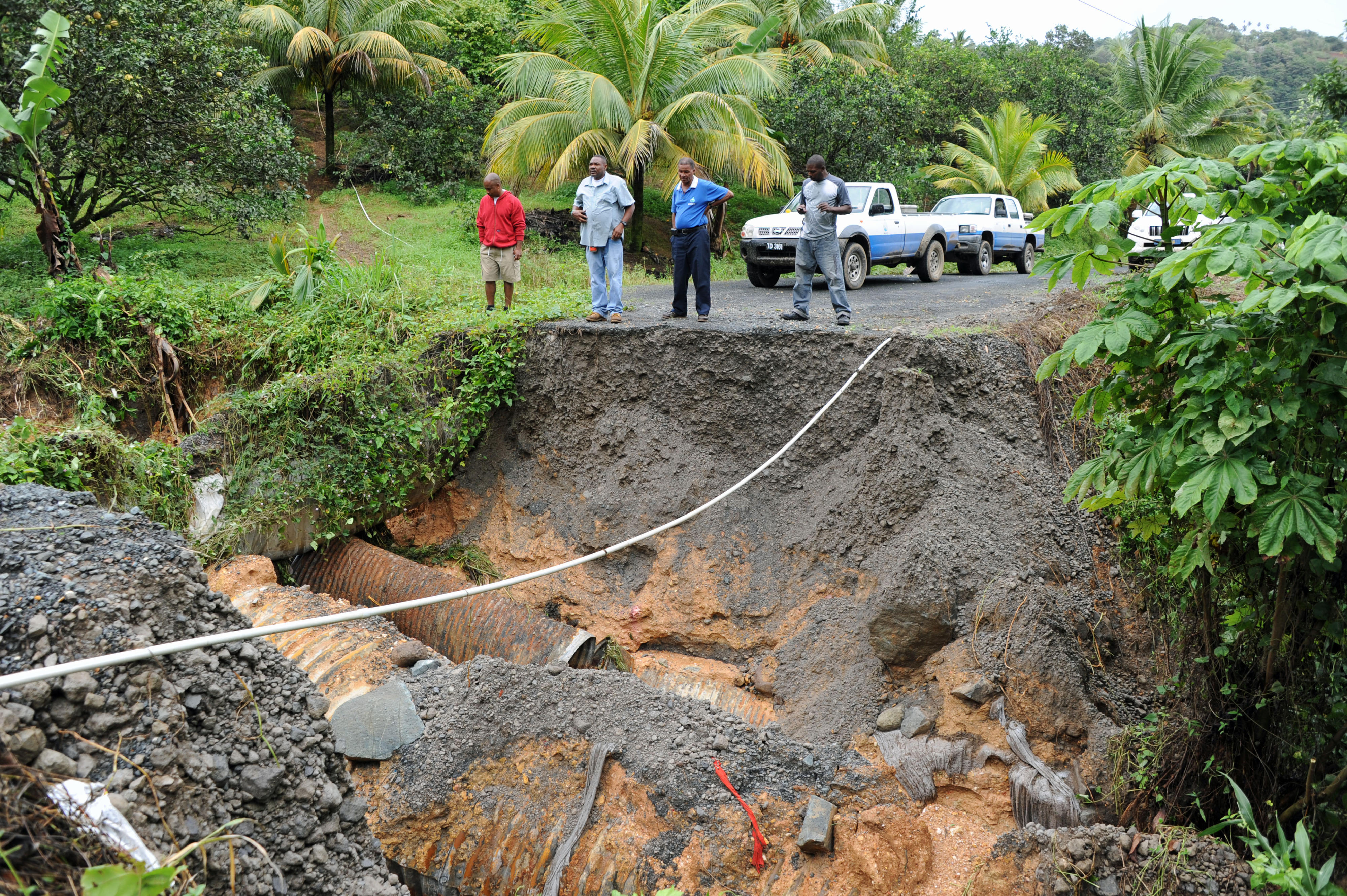
A road in the Caribbean nation of St Lucia was washed away after heavy rain.
Copyright© Horst Vogel / GIZ
Climate change and development policy Protection against loss and damage
The impact of climate change is posing a threat to many people's livelihoods and to sustainable development worldwide. The UN-defined groups of least developed countries (LDCs) and small island developing states (SIDS) – and socially disadvantaged population groups – are hardest hit by this impact. They contribute least to climate change, yet often they do not have the resources needed to deal with its impacts.
That is why the BMZ is putting a strong focus on assisting people and countries in adapting to the consequences of climate change and becoming more resilient to its impacts.
However, in some cases adaptation measures are simply not affordable, or unacceptable to the public, or technically not feasible. In such instances, climate change may result in economic losses and damages such as crop failure from droughts and destruction of homes and businesses by storms. In addition, there are non-economic losses and damages such as displacement, ecosystem loss, and loss of traditions, languages, and people's living environments. Such losses and damages often affect people for many generations – their options in life, their food security, and the social stability of their communities.
Germany is addressing this through its development policy, assisting countries and people in preparing for risks, preventing imminent loss and damage, and protecting themselves against climate-related damage.
Video: Loss and damage
What the BMZ is doing
As the main contributors to climate change, the industrialised countries have a responsibility to lead by example and work towards increasing climate justice. They have pledged to support the efforts of the developing countries to pursue climate-neutral development of their economies and to adapt to those impacts of climate change that can no longer be prevented. Moreover, the industrialised countries are assisting the developing countries in responding to climate change-related loss and damage.
Comprehensive risk management. In order to be able to quickly respond to imminent losses and damages, it is vital to analyse risks early on. The BMZ's comprehensive risk management approach combines strategies and measures to reduce disaster and climate risks. It serves to avert, minimise and address climate change-related loss and damage.
The BMZ pursues a comprehensive approach, relying on both tried-and-tested and innovative instruments for climate change mitigation and adaptation, disaster risk management, climate risk finance, and social protection. The instrument of transitional development assistance provides a stepping stone between humanitarian aid and development cooperation. The purpose of all these efforts is to build long-term resilience, also with a view to the period of post-disaster reconstruction and economic recovery.
Global Shield against Climate Risks. The G7 and the V20 (Vulnerable Twenty, an alliance of countries that are particularly vulnerable to climate change) are jointly developing tools for climate risk protection and preparedness. The Global Shield initiative was launched at the climate conference in Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt, in 2022. Its purpose is to facilitate rapid, needs-based support in response to extreme weather events. The Global Shield is active in Bangladesh, Costa Rica, Gambia, Ghana, Madagascar, Malawi, Pakistan, Peru, Philippines, Rwanda, Senegal, Somalia and the Pacific region.
Implementation of agreements made at international climate negotiations. Under the heading of Loss and Damage, discussions are under way under the umbrella of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) and within the framework of the Paris Agreement on how the international community can respond to loss and damage and how to provide better financial and technical assistance to vulnerable countries in the future. At the 2023 climate conference in Dubai, participants agreed that a support architecture should be set up. The BMZ is working to make sure that the newly established Fund for responding to Loss and Damage (External link) (FRLD) will play an important role in that architecture and strengthen national capacity for dealing with loss and damage. Germany also supports the Santiago Network (External link), which was founded in 2019. Its purpose is to help countries identify technical assistance needs and get in touch with organisations and experts offering relevant expertise.
The BMZ wants to remain involved in giving shape to these global support structures so that they will reach, in particular, those countries and people that are especially affected by climate change.
Climate change-induced migration. Climate change will be displacing more and more people. The BMZ is providing assistance to people faced with situations that force them to migrate.
Biodiversity and climate. Healthy ecosystems such as mangroves and forests provide natural protection against the impacts of climate change. They mitigate the effects of storms, serve as carbon sinks and help to protect people's livelihoods. The BMZ is supporting their protection – as a form of climate action and as a contribution to crisis preparedness.
As at: 01/10/2025