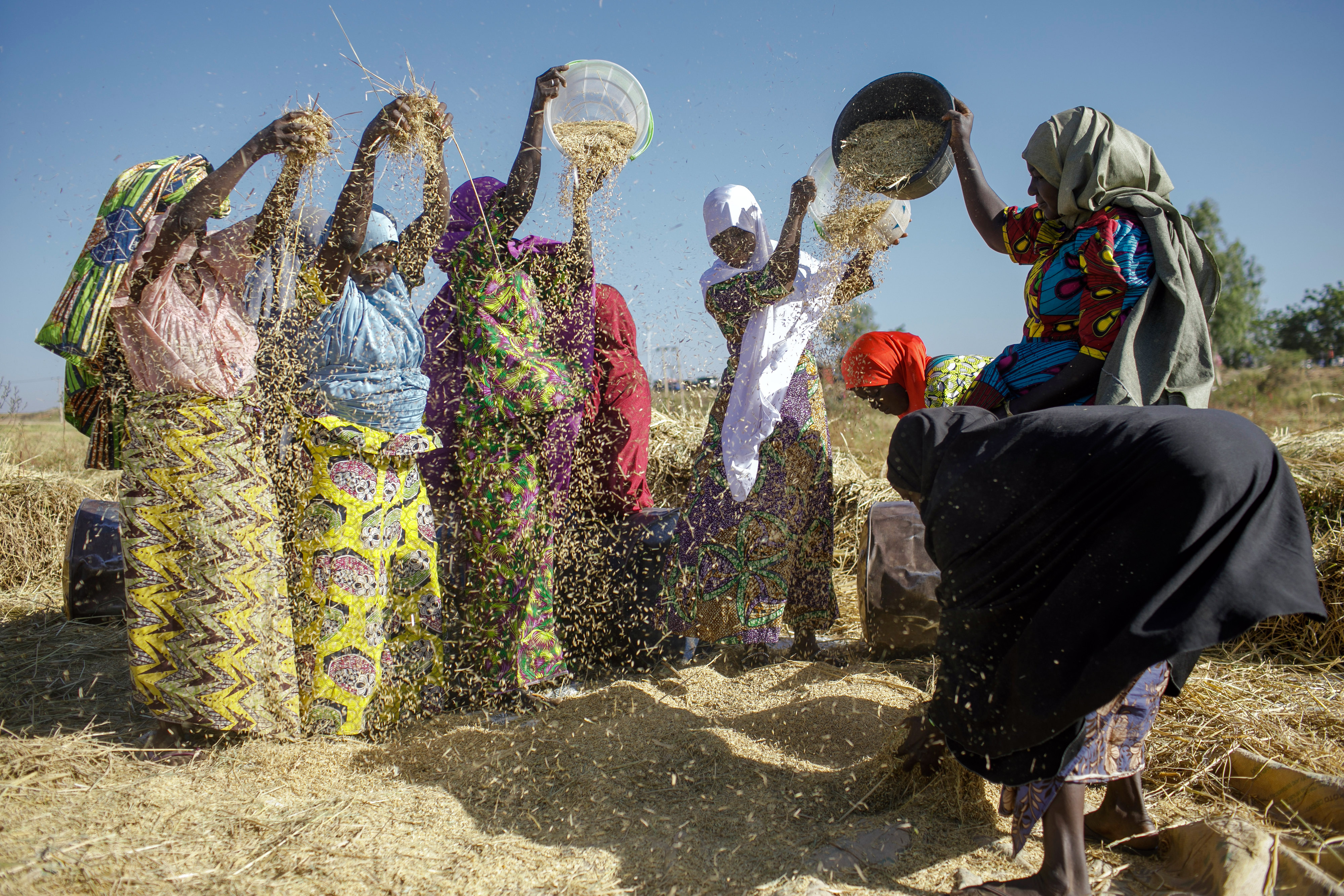
Women threshing rice in Sunu, Nigeria
Copyright© Thomas Imo/photothek.net
Nigeria
In May 2023, Bola Ahmed Tinubu became President. The people of Nigeria and the international community are hoping that he will launch key reform measures and lend new momentum to development.
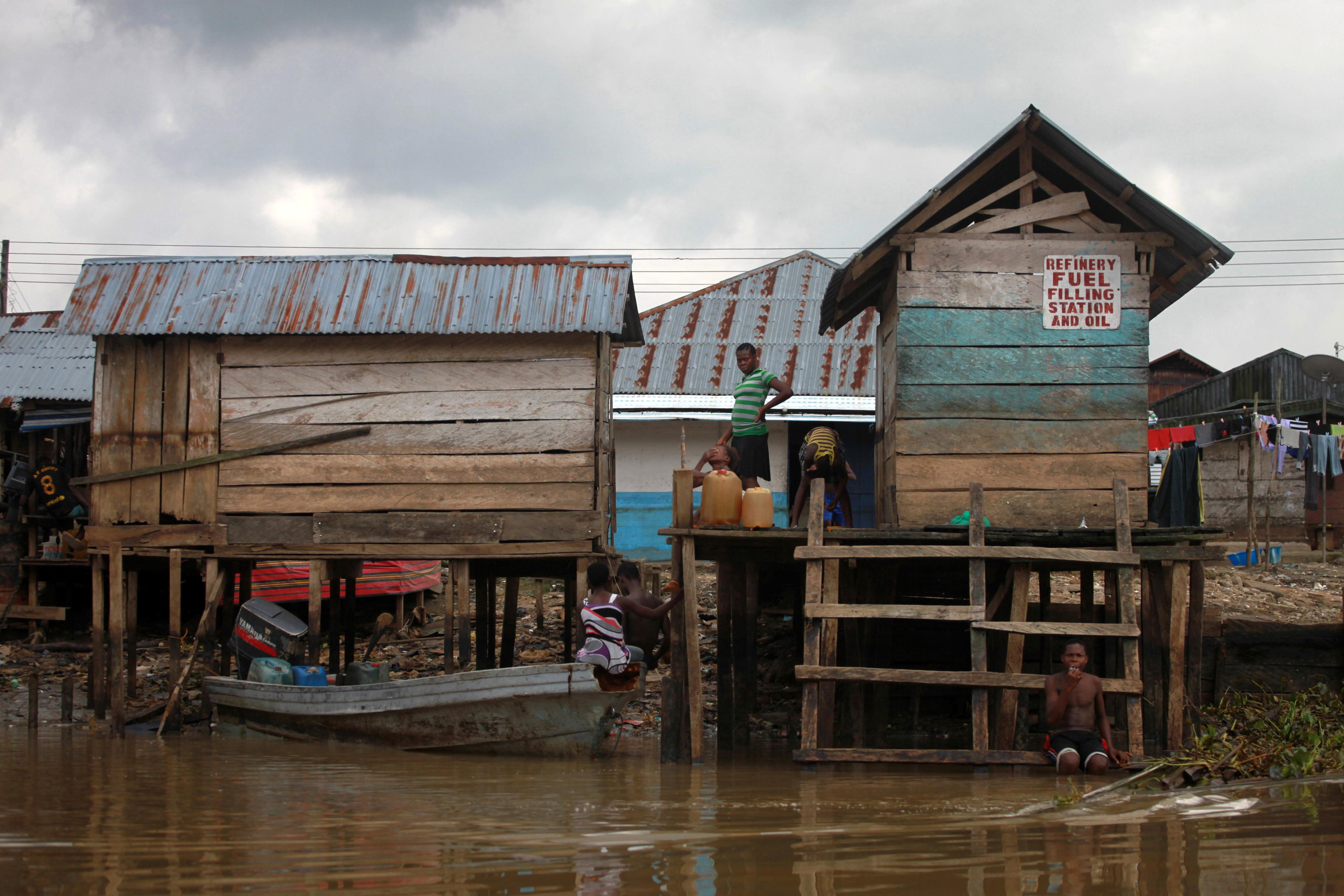
So far, the government of the West African country has not yet succeeded in using the country's wealth of raw materials to foster inclusive economic and social development. On the latest Human Development Index (HDI), Nigeria ranks 164th out of 193 countries.
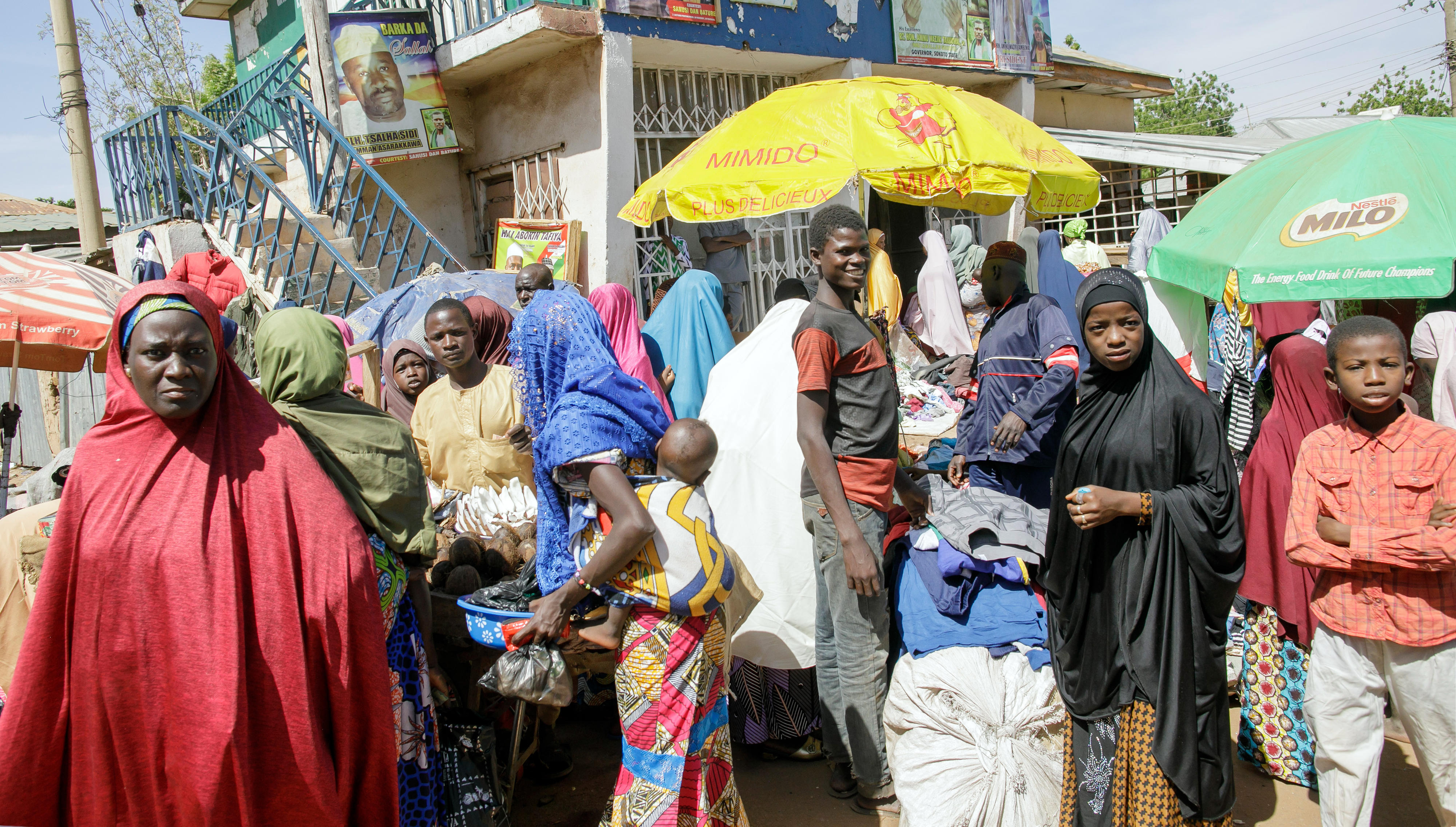
The development of the multi-ethnic country is hampered by social, ethnic and religious conflicts. In addition to a fragile security situation, challenges include high levels of corruption, administrative bodies that lack capacity and transparency, and a lack of economic diversification outside the country's urban centres. Extremely low tax revenues and a high level of public debt are severely restricting the government's capacity for broad-based poverty reduction.
German development cooperation with Nigeria
The overarching goal of Germany's development cooperation with Nigeria is to create employment and a better future for the country's population, which is very young. The Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ) has aligned its cooperation programme with the priorities of the Nigerian government: economic diversification, security, and poverty reduction.
During the government negotiations in October 2022, the BMZ made available a total of 98.5 million euros for Nigeria. The core part of this was 67.5 million euros for Technical Cooperation and Financial Cooperation. The additional funding was provided for a regional food security fund and for the Special Initiatives “Transformation of Agricultural and Food Systems” and “Displaced Persons and Host Countries”.
Nigerian-German development cooperation focuses on the following core areas:
- Sustainable economic development, training and employment
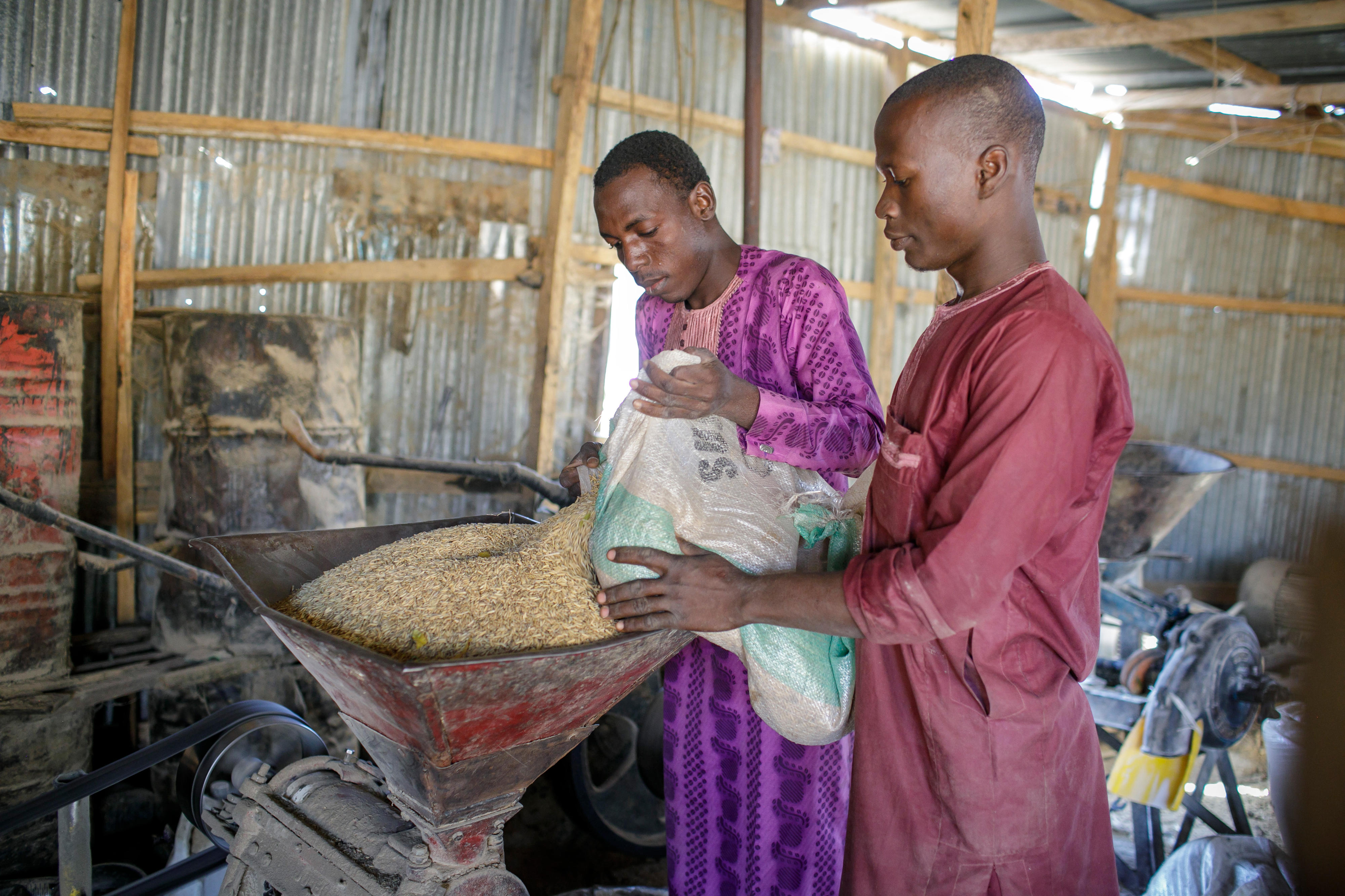
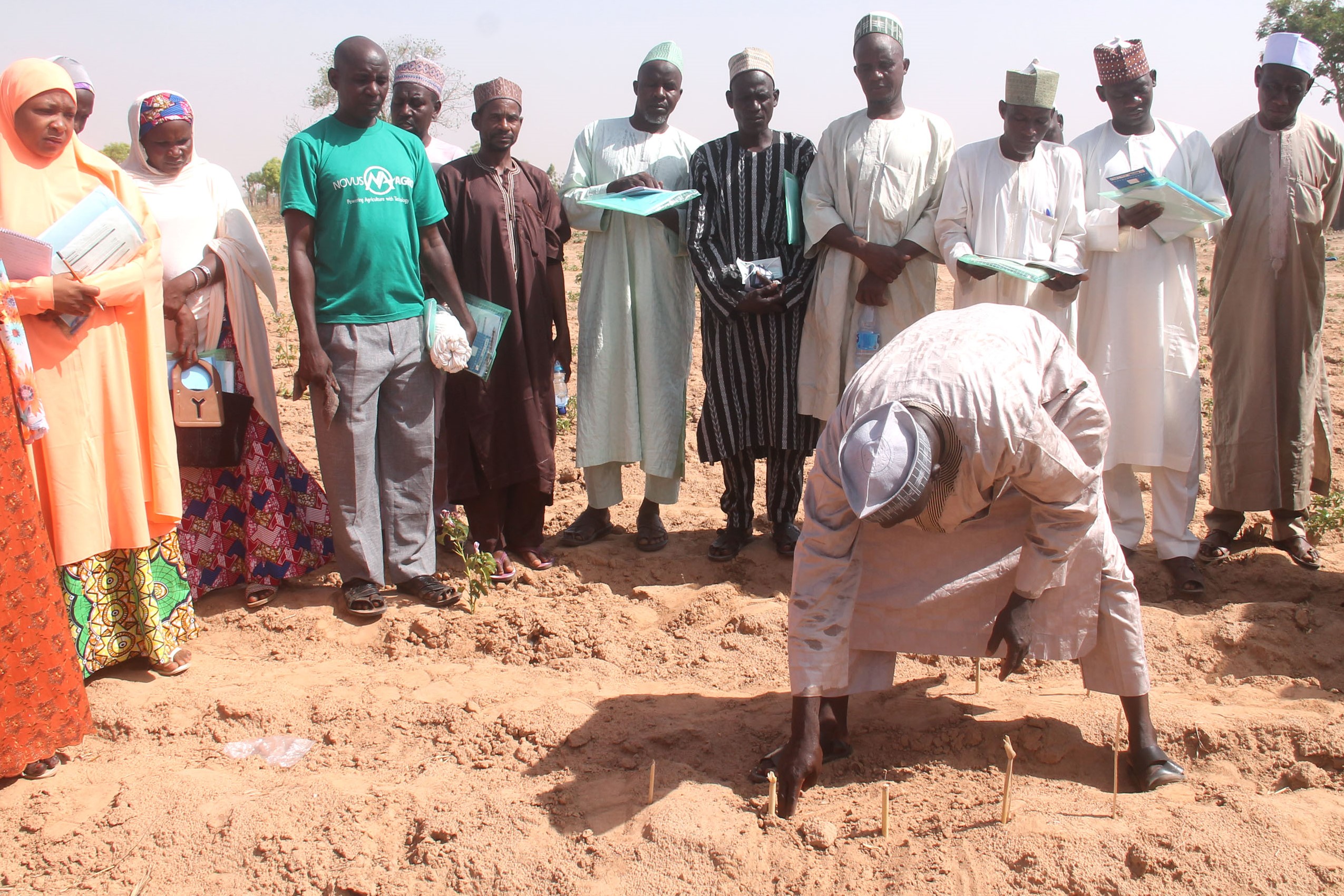
Areas of intervention: technical and vocational education and training, private sector and financial sector development, including the initiative areas “Digital technology and data” and “Making migration work for development” - Transformation of agricultural and food systems
Areas of intervention: rural development, agriculture - Climate and energy, just transition
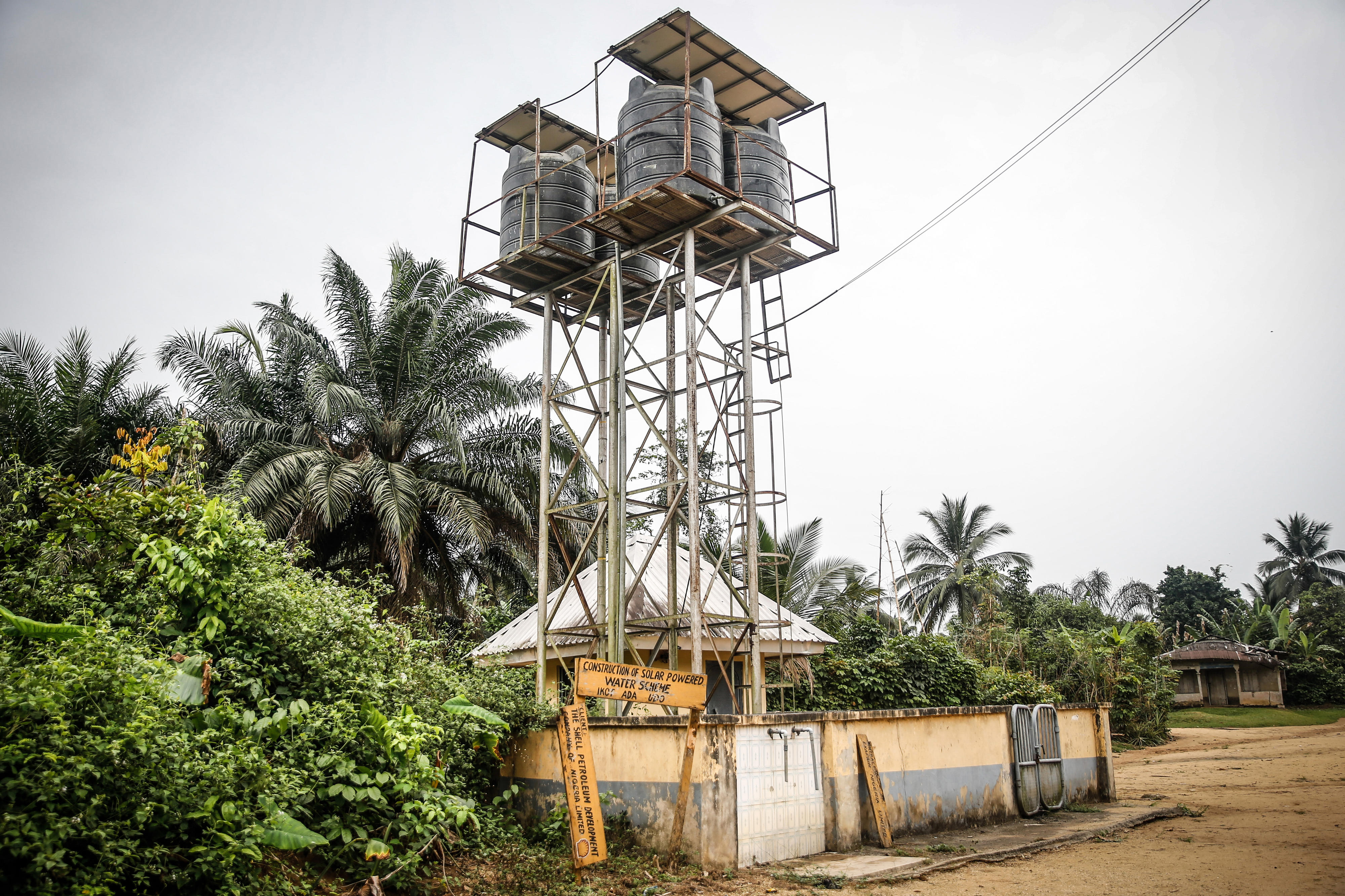
Area of intervention: renewable energy and energy efficiency - Health, social protection and population dynamics
Area of intervention: population dynamics; sexual and reproductive health and rights
Other activities
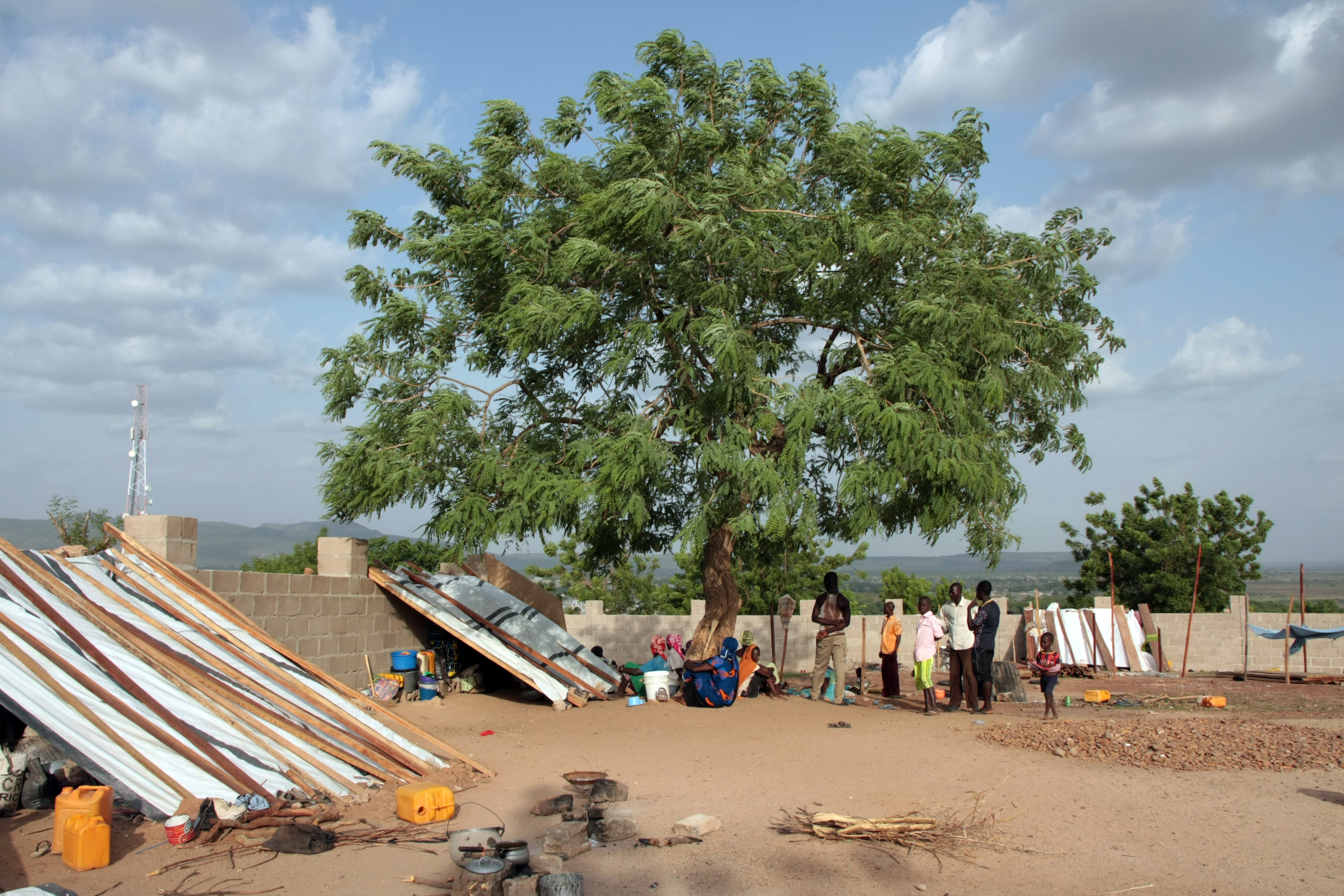
Islamist terrorism, gang crime and conflicts over resources are leading to displacement, lack of security and poverty in Nigeria. In addition to its involvement in the core areas mentioned above, the BMZ therefore assists Nigeria in peacebuilding and conflict prevention. Activities include support for internally displaced people, the development or reconstruction of social infrastructure, and assistance for communities in north-eastern Nigeria that are hosting large numbers of displaced persons. In central Nigeria, development cooperation is supporting efforts to defuse the ethnically and religiously charged conflict over resources between sedentary farmers and nomadic pastoralists.
Germany also supports efforts undertaken by governmental and civil society institutions to fight corruption and facilitate transparent management of government funding.
SDG trends for Nigeria
- On track or maintaining SDG achievement
- Moderately improving
- Stagnating
- Decreasing
- Trend information unavailable